93. Restore IP Addresses
A valid IP address consists of exactly four integers separated by single dots. Each integer is between 0 and 255 (inclusive) and cannot have leading zeros.
- For example,
"0.1.2.201"and"192.168.1.1"are valid IP addresses, but"0.011.255.245","192.168.1.312"and"[email protected]"are invalid IP addresses.
Given a string s containing only digits, return all possible valid IP addresses that can be formed by inserting dots into s. You are not allowed to reorder or remove any digits in s. You may return the valid IP addresses in any order.

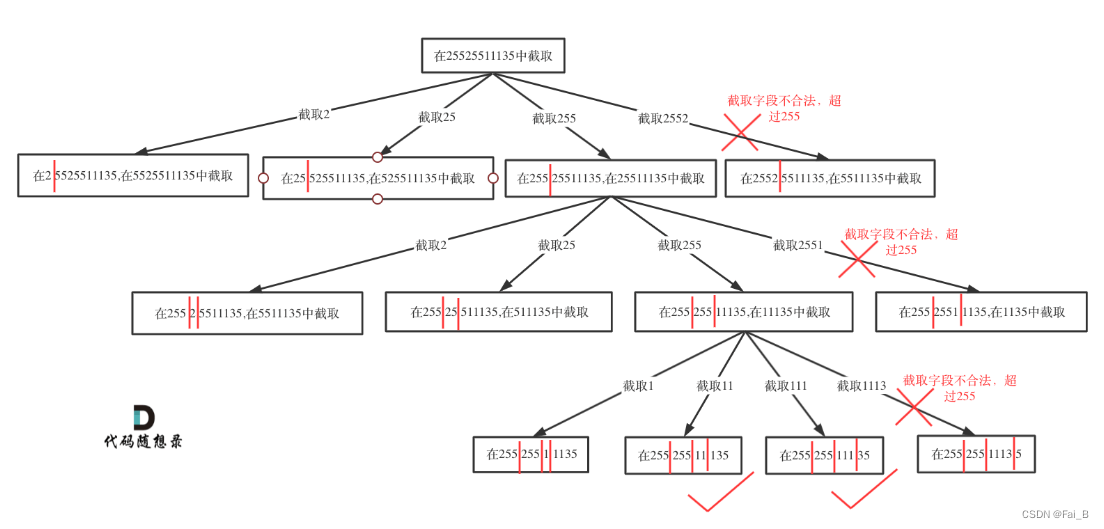
path = ["225", "224"]
result = []
result.append('.'.join(path))
return result #[“225.224”] not [“225”.”224″]
1.pruning: for i in range(index, min(index + 3 , len(s)))
2. def is_valid: 3 conditions !!
backtracking + recursion + pruning:
class Solution:
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s: str) -> List[str]:
result = []
self.backtracking(s, [], result, 0)
return result
def backtracking(self, s, path, result, index):
if len(path) == 4 and index == len(s):
result.append('.'.join(path))
return
if len(path) > 4:
return
for i in range(index, min(index + 3, len(s))): # pruning wrong: len(s)
if self.is_valid(s, index, i):
sub = s[index: i + 1]
path.append(sub)
self.backtracking(s, path, result, i + 1)
path.pop()
def is_valid(self, s, start, end):
if start > end: # 1.
return False
if s[start] == '0' and start != end: #2. '0' cant at the first position
return False
return 0 <= int(s[start : end + 1]) <= 255 # 3.
78. Subsets
Given an integer array nums of unique elements, return all possible subsets (the power set)< /em>.
The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in any order.

1. Termination conditions do not have to if, all conditions meet and you should use append directly
2. The empty set 【】has been append in before the first for loop.
3. No slicing, no need for path. append [index, i].
class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
nums.sort()
result = []
self.backtracking(nums, [], result, 0)
return result
def backtracking(self, nums, path, result, index):
result.append(path[:]) # dont forget [:]
for i in range(index, len(nums)):
path.append(nums[i]) # wrong: nums[index, i + 1] is not a slice
self.backtracking(nums, path, result, i + 1)
path.pop()
90. Subsets II
Given an integer array nums that may contain duplicates, return all possible subsets
(the power set).
The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in any order.

duplicates
1. if path not in result: (slow)
class Solution:
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
result = []
nums.sort()
self.backtracking(nums, [], result, 0)
return result
def backtracking(self, nums, path, result, startindex):
if path not in result:
result.append(path[:])
for i in range(startindex, len(nums)):
path.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, path, result, i + 1)
path.pop()
2. Use recursion when the next startIndex is i + 1 instead of 0 to remove duplication
if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i – 1]:
continue
class Solution:
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
result = []
path = []
nums.sort() # Deduplication requires sorting
self.backtracking(nums, 0, path, result)
return result
def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, path, result):
result.append(path[:]) # Collect subsets
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
# And we need to skip elements used in the same tree layer
if i > startIndex and nums[i] == nums[i - 1]:
continue
path.append(nums[i])
self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, path, result)
path.pop()
3.Using used arrays for de-duplication
class Solution:
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
result = []
path = []
used = [False] * len(nums)
nums.sort() # Deduplication requires sorting
self.backtracking(nums, 0, used, path, result)
return result
def backtracking(self, nums, startIndex, used, path, result):
result.append(path[:]) # Collect subsets
for i in range(startIndex, len(nums)):
# used[i - 1] == True, indicating that the same branch nums[i - 1] has been used
# used[i - 1] == False, indicating that the same tree layer nums[i - 1] has been used
# And we need to skip elements used in the same tree layer
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i - 1] and not used[i - 1]:
continue
path.append(nums[i])
used[i] = True
self.backtracking(nums, i + 1, used, path, result)
used[i] = False
path.pop()
4.use set()